Network Automation & Cybersecurity
Efficiency Through Automation, Protection Through Innovation.
What is network automation?
Industrial Cybersecurity Solutions
Why automate your network?
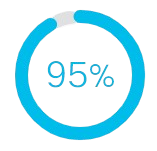
Up to 95 percent of network changes today are done manually.

Manual changes lead to configuration errors and inconsistencies in the network.

Expanding network changes at scale can be problematic.

Network downtime and nonremote troubleshooting time are detrimental.
Find the path to automation that's right for you
With network automation, you’ll quickly and easily design, provision, and apply policy across your network. And in your journey to automation, you choose the path and the pace. Work with existing network and policy definitions, migrate as fast or slow as you’d like, or start from scratch.
Whatever your path, the MetaNEXTGen Customer Experience team can help you strategize, deploy, and manage your network.
Step 1: network design
- Quick, clear visibility of network devices and clients.
- Map and logical views.
- Importing with Prime Infrastructure, losing none of your former work.
Step 2: profiles and policies
- Applications and services that follow policies created.
- Network performance that aligns with business intent.
Step 3: provisioning and connecting
- Zero-touch provisioning of off-the-shelf devices.
- Easy control of device configurations for consistency and accuracy.
Step 4: automated lifecycle management
- Fast and accurate deployment of patches and updates.
- Systemwide configuration updates as driven by assurance.
Related solutions for network automation
Enterprise networking
MetaNEXTGen networking automation capabilities transform previously manual onboarding, configuration, provisioning, and software management processes to simplify and scale network operations and greatly minimize configuration errors.
Data center networking
From programmable infrastructure, to single-pane of glass management and common policy for data center operations, MetaNEXTGen provides network automation tools to seamlessly move apps and data between on-premises data centers and clouds.
Service providers
MetaNEXTGen intent-based, closed-loop automation portfolio offers service providers comprehensive solutions for full-lifecycle network management to improve agility, scalability, operational excellence, and customer experience.

Why MetaNEXTGen for network automation?
Made to work together
MetaNEXTGen offerings are made to work together to provide you with the elements you need for network automation.
Migrate at your own speed
Migrate at a pace that makes you comfortable. Import your former work on device mapping and policies.
Comprehensive solutions + software + products + services
Software defines how our hardware, software, fabric digital automation, and nonfabric base automation work together.
No other vendor can deliver like MetaNEXTGen
Only MetaNEXTGen can deliver IBNs that leverage automation, intelligence, and human expertise in such a way that helps simplify complexity, optimize IT, and reduce operational costs.
What is cybersecurity?

What is cybersecurity all about?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. These cyberattacks are usually aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information; extorting money from users through ransomware; or interrupting normal business processes.
Implementing effective cybersecurity measures is particularly challenging today because there are more devices than people, and attackers are becoming more innovative.
A successful cybersecurity posture has multiple layers of protection spread across the computers, networks, programs, or data that one intends to keep safe. In an organization, a unified threat management gateway system can automate integrations across products and accelerate key security operations functions: detection, investigation, and remediation. People, processes, and technology must all complement one another to create an effective defense from cyberattacks.
People
Processes
Technology
Why is cybersecurity important?
In today’s connected world, everyone benefits from advanced cybersecurity solutions. At an individual level, a cybersecurity attack can result in everything from identity theft to extortion attempts, to the loss of important data like family photos. Everyone relies on critical infrastructure like power plants, hospitals, and financial service companies. Securing these and other organizations is essential to keeping our society functioning.
Everyone also benefits from the work of cyberthreat researchers, like the team of 250 threat researchers at Talos, who investigate new and emerging threats and cyberattack strategies. They reveal new vulnerabilities, educate the public on the importance of cybersecurity, and strengthen open-source tools. Their work makes the internet safer for everyone.

Types of cybersecurity threats
Cloud security
Identity
Identity security and access management involve safeguarding the digital identities of individuals, devices, and organizations. This involves implementing security processes, tools, and policies that control user access to accounts and enable productivity with frictionless access to important information without risk.
The three main goals of identity security are to:
- Authenticate a user’s identity
- Authorize access to appropriate resources
- Monitor access activity for weak posture and suspicious activity
Malware
Malware is a type of software designed to gain unauthorized access or to cause damage to a computer.
Phishing
Phishing is the practice of sending fraudulent emails that resemble emails from reputable sources. The aim is to steal sensitive data, such as credit card numbers and login information, and is the most common type of cyberattack. You can help protect yourself through education or a technology solution that filters malicious emails.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that is designed to extort money by blocking access to files or the computer system until the ransom is paid. Paying the ransom does not guarantee that the files will be recovered or the system restored.
Social engineering
Social engineering is a tactic that adversaries use to trick you into revealing sensitive information. Attackers can solicit a monetary payment or gain access to your confidential data. Social engineering can be combined with any of the threats mentioned above to make you more likely to click on links, download malware, or trust a malicious source.
Threat detection
Zero trust
Zero trust isn’t a single product or technology. It’s a security strategy that is best implemented by keeping an organization’s business operations, risks, and security outcomes in mind. Although there are various paths to achieving zero trust maturity, most organizations prioritize deployment of technologies such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), device posture checks, zero trust network access (ZTNA), and network segmentation as they implement zero-trust security.

Best practices for cybersecurity
Adopting best practices for cybersecurity can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
Here are three key practices:
Regular software and operating system updates
Updating software and operating systems regularly helps to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security measures against potential threats.
Using strong and unique passwords
Creating strong and unique passwords for each online account can enhance cybersecurity, as cyberattacks often exploit weak or stolen passwords.
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication involves multiple identification forms before account access, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Cisco Duo includes MFA that can integrate with most major applications as well as custom apps.
